Secret Benefits of Using Concrete Scanning Modern Technology
Secret Benefits of Using Concrete Scanning Modern Technology
Blog Article
Introduce the Transformative Power of Concrete Scanning in Maximizing Effectiveness and Security
Concrete scanning has actually arised as an essential device in the building and construction sector, offering exceptional advantages in enhancing project performance and making sure safety and security standards. By using advanced innovation, concrete scanning permits experts to see beyond the surface, uncovering hidden complexities that might affect the structural integrity of a structure. The transformative power of concrete scanning exists in its capacity to offer detailed insights and real-time data, transforming how projects are planned and performed. As we look into the intricacies of this cutting-edge method, a globe of opportunities opens, showcasing a new era of building and construction techniques that focus on accuracy and safety.
Significance of Concrete Scanning
Guaranteeing the structural stability and safety and security of building and construction tasks begins with the critical action of carrying out thorough concrete scanning. Concrete scanning is a non-destructive approach used to find and map subsurface elements within concrete structures.
The significance of concrete scanning can not be overstated, as it plays an essential duty in protecting against accidents, decreasing task delays, and guaranteeing the long-lasting sturdiness of the building. By identifying potential threats before the building and construction stage begins, builders can implement ideal security steps and make notified decisions regarding the design and execution of the job. Additionally, concrete scanning helps in enhancing job timelines and budget plan by preventing unexpected prices and hold-ups that may develop due to unforeseen blockages within the concrete. Inevitably, investing in detailed concrete scanning is a proactive approach that boosts both effectiveness and safety in building tasks.
How Concrete Scanning Works
Concrete scanning operates as an important device in building and construction jobs by utilizing sophisticated innovations to spot and map subsurface elements without causing architectural damages. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) are 2 key techniques made use of in concrete scanning.
During the scanning procedure, the information collected is evaluated in real-time, permitting instant identification of prospective dangers or obstacles below the surface area. By employing these advanced modern technologies, concrete scanning considerably minimizes the risk of costly damages and injuries on building sites.
Benefits of Concrete Scanning
Making use of sophisticated scanning innovations in building and construction tasks uses a wide range of advantages, boosting both effectiveness and safety on-site. One of the key benefits of concrete scanning is the capacity to identify and find ingrained objects such as rebar, post-tension cable televisions, and channels accurately. By recognizing these components prior to exploration or cutting right into concrete structures, the danger of unintended strikes is significantly lowered, protecting against potential injuries to workers and damage to the structure itself. Furthermore, concrete scanning assists in preparation and designing better, as it provides accurate information regarding the location and deepness of structural components.

Case Studies: Concrete Scanning Success
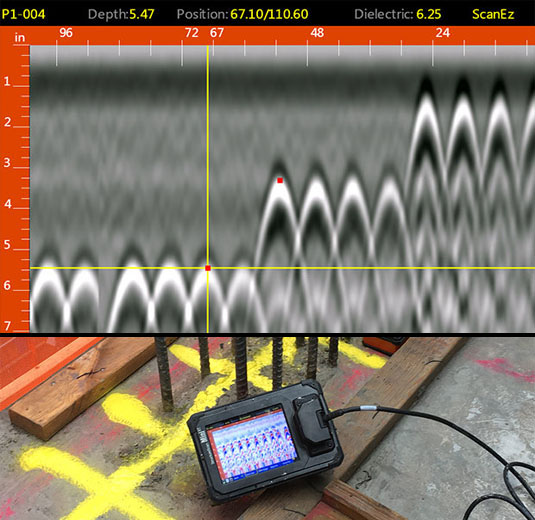
In one more case, a building firm made use of 3D concrete scanning to evaluate the condition of aging concrete frameworks in a historic building. The in-depth scans given valuable insights right into the level of wear and tear and aided focus on maintenance efforts efficiently. By proactively attending to areas helpful resources of issue recognized via scanning, the company was able to prolong the life-span of the structure and make sure owner safety.
These case research studies emphasize the transformative power of concrete scanning in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and safety in building jobs.
Applying Concrete Scanning in Projects
Implementing advanced scanning innovations during construction tasks has actually come to be progressively important for enhancing precision and safety. By incorporating concrete scanning into project planning and execution, building and construction groups can determine prospective dangers, such as rebar or post-tension cords, hidden within concrete structures. This positive technique reduces the risk of accidents, hold-ups, and costly rework, inevitably causing extra reliable job timelines and budget plans.
To implement concrete scanning efficiently, project supervisors ought to collaborate very closely with seasoned scanning specialists to determine one of the most appropriate scanning techniques for the specific task demands. Engaging scanning experts from the very early stages of a project makes it possible for the group to produce extensive scanning plans that address crucial areas of concern and ensure complete data collection.
Moreover, including concrete scanning into normal job process can streamline decision-making procedures, as real-time scan data provides instant understandings into the problem of concrete structures - Concrete Scanning. This data-driven technique helps with educated analytic and allows groups to make modifications without delay, cultivating a culture of effectiveness and security throughout the project lifecycle

Conclusion
In go to website verdict, concrete scanning plays an essential duty in boosting efficiency and security in building and construction tasks. By utilizing innovative innovation to detect and map out underlying structures within concrete, this process assists to stop costly errors, ensure structural honesty, and decrease threats on website. With the capacity to reveal surprise components and provide exact information, concrete scanning proves to be an important tool for enhancing project results and taking full advantage of total success.
Concrete scanning is a non-destructive technique made use of to find and map subsurface components within concrete frameworks. Furthermore, concrete scanning aids in maximizing task timelines and budget by staying clear of unanticipated prices and hold-ups that might arise due to unexpected obstructions within the concrete. One notable instance research entails a large renovation task where concrete scanning played an important role in ensuring project success.In an additional instance, a building and construction business utilized 3D concrete scanning to assess the problem of maturing concrete structures in a historical structure. By incorporating concrete scanning into project preparation and implementation, construction groups can recognize prospective hazards, such as rebar or post-tension cables, concealed within concrete structures.
Report this page